As the oil and gas industry faces increasing scrutiny over environmental impacts, effective drilling waste management has become a priority. Recycling plays a vital role in mitigating the adverse effects of drilling operations while promoting sustainability and cost efficiency. This article explores the importance of recycling in drilling waste management, the technologies involved, and its broader implications for the industry.
Understanding Drilling Waste Management
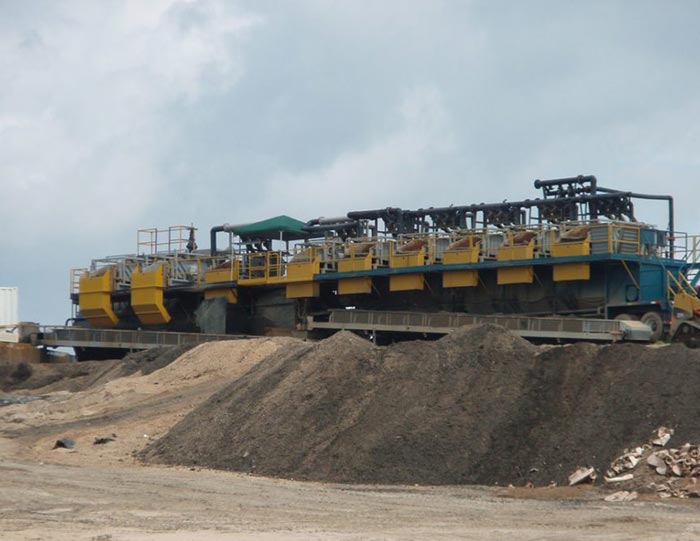
Drilling waste encompasses various materials generated during drilling operations, including drilling fluids, cuttings, and other solid waste. These materials can pose significant environmental risks if not managed properly. The conventional disposal methods, such as landfilling or direct discharge into the environment, are increasingly viewed as unsustainable. Consequently, the industry is shifting towards recycling as a means to minimize waste and enhance environmental stewardship.
The Importance of Recycling With Drilling Waste Management
Recycling in drilling cuttings waste management offers several benefits. Firstly, it significantly reduces the volume of waste sent to landfills. By recovering valuable materials and fluids, companies can decrease their reliance on disposal methods that may be harmful to the environment. This not only aligns with regulatory requirements but also enhances the overall sustainability of drilling operations.
Secondly, recycling can lead to substantial cost savings. The recovery and reuse of drilling fluids, for instance, can lower operational costs by reducing the need to purchase new materials. This is particularly significant in an industry where margins are often tight, and operational efficiency is crucial.
Furthermore, recycling supports the principles of a circular economy. By reintroducing materials back into the production cycle, the industry can reduce its resource consumption and lower its carbon footprint. This shift towards sustainable practices is essential as the world increasingly demands responsible resource management.
Technologies for Recycling Drilling Waste
Several technologies facilitate the recycling of drilling waste, each tailored to specific types of waste materials. One of the most common methods is the use of centrifuges, which separate solids from liquids in drilling fluids. This technology allows for the recovery of valuable drilling fluids for reuse while producing solid waste that can be further treated or disposed of safely.
Another innovative approach is thermal desorption, which involves heating drilling cuttings to evaporate the contained fluids, allowing for the separation of oil-based and water-based materials. This process not only recycles the fluids but also reduces the volume of hazardous waste, making it easier to manage.
Additionally, advancements in bioremediation are emerging as an effective method for treating contaminated drilling waste. By employing naturally occurring microorganisms to break down hazardous components, bioremediation helps detoxify waste materials, enabling their safe disposal or reuse.
Case Studies of Successful Recycling Programs About Drilling Waste Management
Numerous companies have successfully implemented recycling programs that illustrate the effectiveness of these technologies. For example, a major operator in the North Sea has adopted a comprehensive recycling strategy that includes both centrifugation and thermal desorption. This dual approach allows the company to recover over 80% of its drilling fluids for reuse, significantly reducing waste and costs.
In Texas, another operator implemented a landfill diversion program that achieved a diversion rate of over 70%. By collaborating with local recycling facilities, the company effectively processed and reused solid waste, demonstrating the potential of community partnerships in advancing recycling efforts.
These case studies not only highlight the feasibility of recycling technologies but also emphasize the importance of adopting a proactive approach to waste management.
Overcoming Challenges in Recycling With Drilling Waste Management
Despite the clear benefits of recycling, the industry faces several challenges. One major hurdle is the initial investment in recycling technologies, which can be significant. However, many operators find that the long-term savings and environmental benefits far outweigh these upfront costs.
Additionally, there is often a lack of infrastructure for recycling drilling waste, particularly in remote locations. To address this issue, companies may need to invest in mobile recycling units that can be deployed at various drilling sites, ensuring that recycling is feasible regardless of location.
Moreover, industry-wide collaboration and knowledge sharing are essential for overcoming these challenges. By working together, companies can develop best practices, share resources, and foster innovation in recycling technologies.
The Future of Recycling in Drilling Waste Management
As the oil and gas industry continues to evolve, recycling will play an increasingly central role in drilling waste management. Regulatory pressures are likely to tighten, pushing companies to adopt more sustainable practices. Moreover, the growing emphasis on corporate social responsibility will drive operators to demonstrate their commitment to environmental stewardship.
The integration of advanced technologies, such as artificial intelligence and machine learning, may also enhance recycling efforts. These technologies can optimize recycling processes, improve waste tracking, and enable real-time monitoring of recycling efficiency, further enhancing sustainability in drilling operations.
 Linear Motion Shale Shaker In Drilling Rig
Linear Motion Shale Shaker In Drilling Rig  Oilfield Mud Cleaner
Oilfield Mud Cleaner  Drilling Fluid Decanter Centrifuge
Drilling Fluid Decanter Centrifuge Drilling Mud Desander
Hydrocyclone Desilter
Centrifugal Pump/Centrifugal Mud Pump
Shear Pump
Jet Mud Mixer
Horizontal Mud Agitator
Constant Pressure Drilling Fluid Mud Gas Separator
Mud Gun
 Mud Tank
Mud Tank Solids Control System Vacuum Degasser
 Flare Ignition Device
Flare Ignition Device  Diesel Tank
Diesel Tank  Submersible Slurry Pump
Submersible Slurry Pump