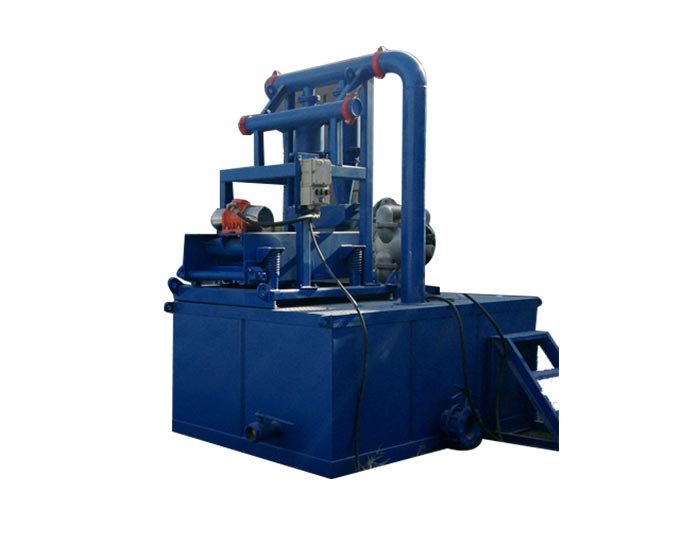
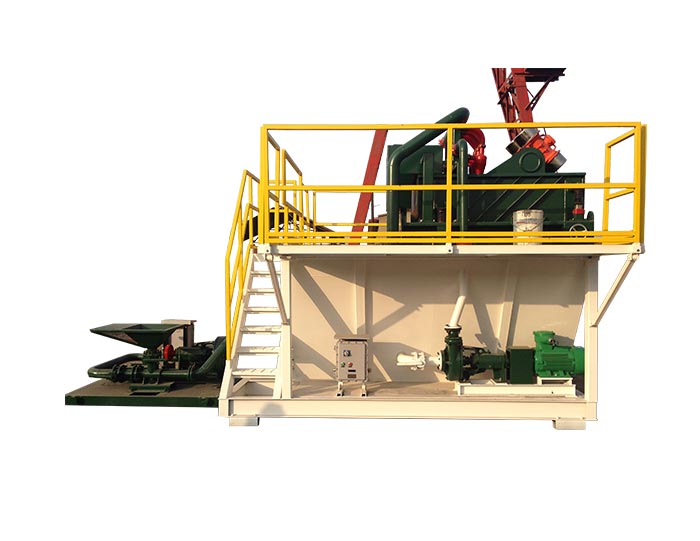
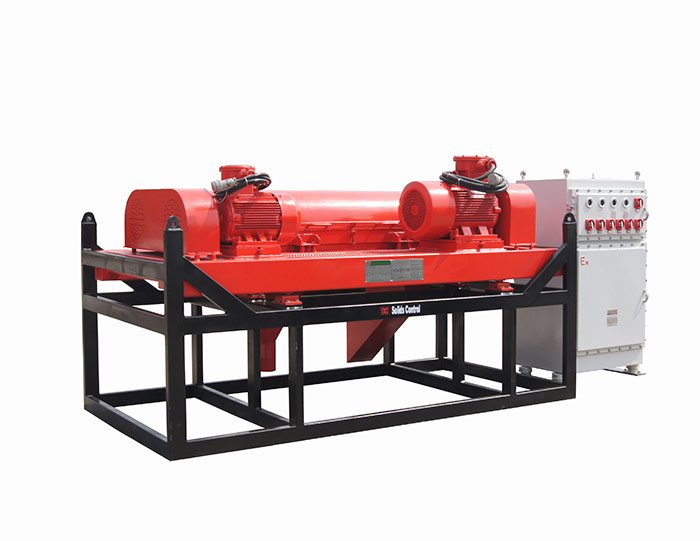
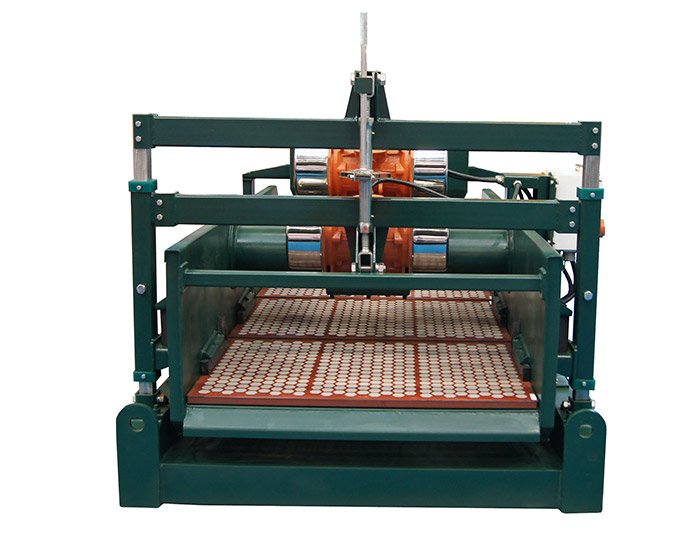
The drilling industry is continuously evolving, and one of the critical areas experiencing significant advancements is drilling mud recycling systems. As the demand for sustainable and efficient drilling practices grows, innovative technologies are being developed to optimize the recycling of drilling mud. These technologies not only enhance operational efficiency but also contribute to environmental sustainability. This article explores some of the latest innovations in drilling mud recycling systems and their implications for the industry.
Understanding Drilling Mud Recycling
Drilling mud, or drilling fluid, is essential in various drilling operations, serving functions such as cooling and lubricating the drill bit, transporting cuttings, and stabilizing the wellbore. However, managing this material can pose challenges, particularly regarding waste disposal and environmental impact. Drilling mud recycling involves the treatment and reuse of drilling fluids, allowing for the reduction of waste and the conservation of resources.
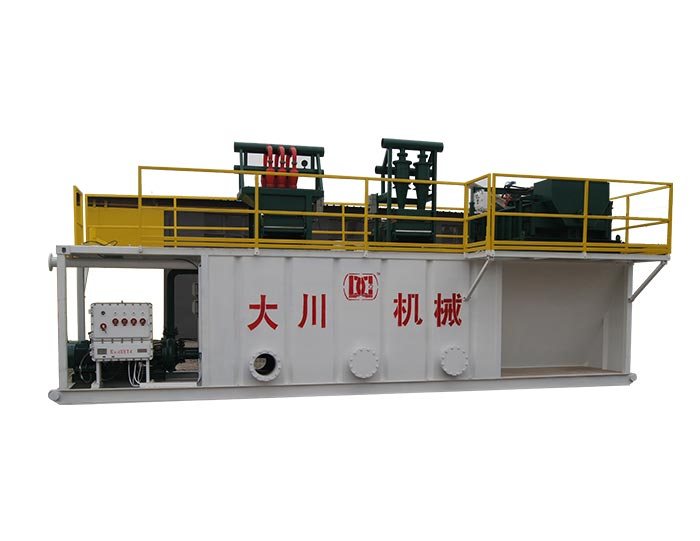
Innovative technologies in mud recycling are designed to improve the efficiency of this process, enabling operators to reclaim and reuse drilling fluids more effectively. The integration of advanced systems not only enhances the quality of recycled mud but also reduces operational costs and environmental risks.
Advanced Separation Technologies About Drilling Mud Recycling Systems
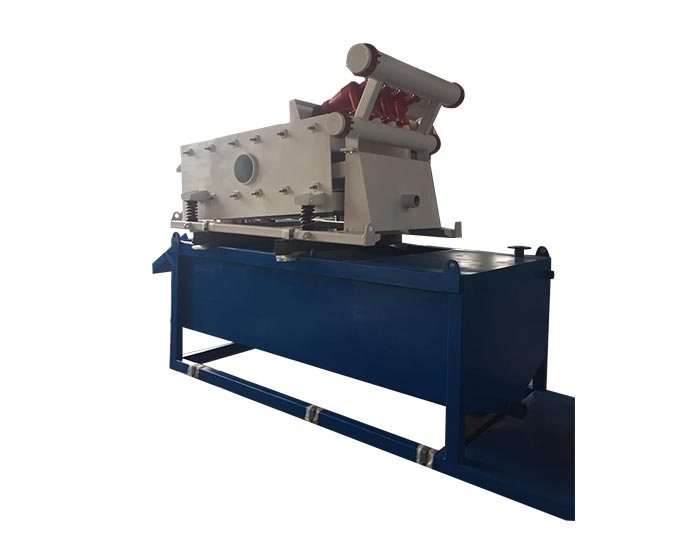
One of the most significant advancements in drilling mud system is the development of advanced separation technologies. These systems are designed to effectively separate solid particles from the drilling fluid, allowing for the reclamation of usable mud. Traditional separation methods often struggle with fine particles, which can affect the performance of recycled mud.
Newer technologies, such as high-speed centrifuges and advanced hydrocyclones, have emerged to address these challenges. High-speed centrifuges utilize centrifugal force to separate solids from liquids more efficiently, resulting in cleaner recycled fluid. Hydrocyclones, on the other hand, use a combination of centrifugal force and gravity to achieve effective separation. These technologies can significantly enhance the quality of recycled drilling mud, ensuring it meets the necessary performance standards for reuse.
Smart Monitoring Systems About Drilling Mud Recycling Systems
The integration of smart monitoring systems into mud circulation system processes is another innovative development. These systems leverage real-time data analytics to monitor the properties of drilling mud, such as viscosity, density, and chemical composition. By continuously assessing these parameters, operators can make informed decisions regarding the recycling process, ensuring optimal performance and quality of the recycled fluid.
Smart monitoring systems can also provide predictive analytics, allowing operators to anticipate potential issues before they arise. This proactive approach enables timely interventions, reducing downtime and enhancing overall efficiency. The use of IoT (Internet of Things) technology further enhances these systems, enabling remote monitoring and control, which is particularly valuable in remote drilling locations.
Enhanced Chemical Treatments With Drilling Mud Recycling Systems
Chemical treatments play a crucial role in the effectiveness of drilling mud recycling. Innovative chemical additives are being developed to enhance the properties of recycled mud, ensuring it performs effectively in various drilling conditions. These additives can improve the stability, lubricity, and filtration control of recycled drilling fluids, making them suitable for reuse.
Moreover, advancements in eco-friendly chemical formulations are gaining traction. Biodegradable and non-toxic additives are being introduced to minimize environmental impact while maintaining the performance of recycled mud. This shift towards more sustainable chemical treatments aligns with the industry's growing focus on environmental responsibility and compliance with regulatory standards.
Closed-Loop Recycling Systems About Drilling Mud Recycling Systems
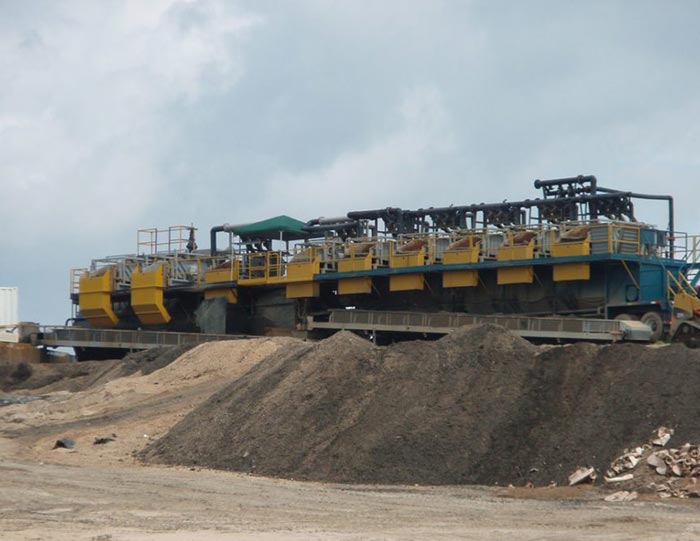
Closed-loop recycling systems represent a significant leap forward in drilling mud management. Unlike traditional systems, which may discharge waste fluids into the environment, closed-loop systems recirculate drilling mud within the drilling operation. This approach minimizes waste generation and allows for continuous reuse of the drilling fluid.
These systems are designed to handle a wide range of drilling conditions and mud types, making them versatile and efficient. By maintaining a closed-loop system, operators can significantly reduce the environmental footprint of their drilling operations while also lowering costs associated with waste disposal and new fluid purchases.
Automation and Robotics About Drilling Mud Recycling Systems
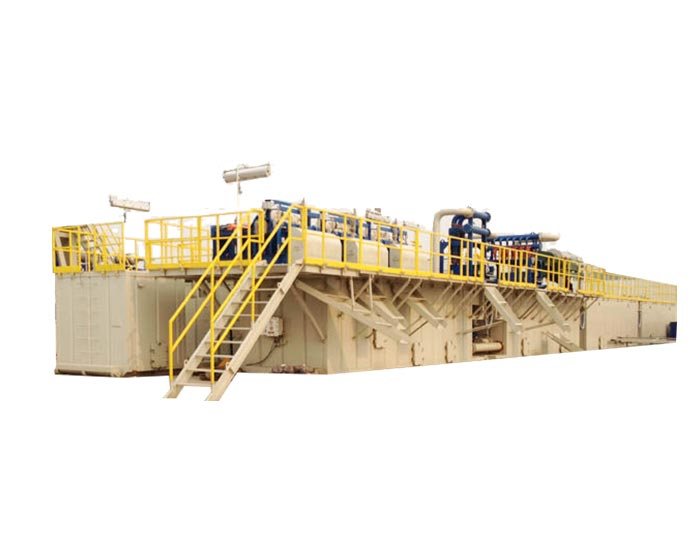
The incorporation of automation and robotics into drilling mud recycling systems is another exciting development. Automated systems can streamline the recycling process, reducing the need for manual labor and minimizing human error. For instance, robotic systems can be deployed to monitor fluid properties, perform routine maintenance, and manage the separation processes, allowing for more precise and efficient operations.
Automation also enhances safety by reducing the risk of accidents associated with manual handling of hazardous materials. As the technology continues to advance, the potential for fully automated drilling mud recycling systems is becoming more feasible, promising even greater efficiencies and safety in drilling operations.
Training and Knowledge Sharing With Drilling Mud Recycling Systems
Innovative technologies in drilling mud recycling also highlight the importance of training and knowledge sharing within the industry. As new systems and processes are implemented, it is crucial for personnel to be adequately trained in their operation and maintenance. Continuous education ensures that staff can effectively utilize these technologies, maximizing their potential benefits.
Additionally, sharing best practices and experiences among industry stakeholders fosters a collaborative approach to innovation. By learning from one another, companies can refine their mud recycling processes and develop new solutions to common challenges.
 Linear Motion Shale Shaker In Drilling Rig
Linear Motion Shale Shaker In Drilling Rig  Oilfield Mud Cleaner
Oilfield Mud Cleaner  Drilling Fluid Decanter Centrifuge
Drilling Fluid Decanter Centrifuge Drilling Mud Desander
Hydrocyclone Desilter
Centrifugal Pump/Centrifugal Mud Pump
Shear Pump
Jet Mud Mixer
Horizontal Mud Agitator
Constant Pressure Drilling Fluid Mud Gas Separator
Mud Gun
 Mud Tank
Mud Tank Solids Control System Vacuum Degasser
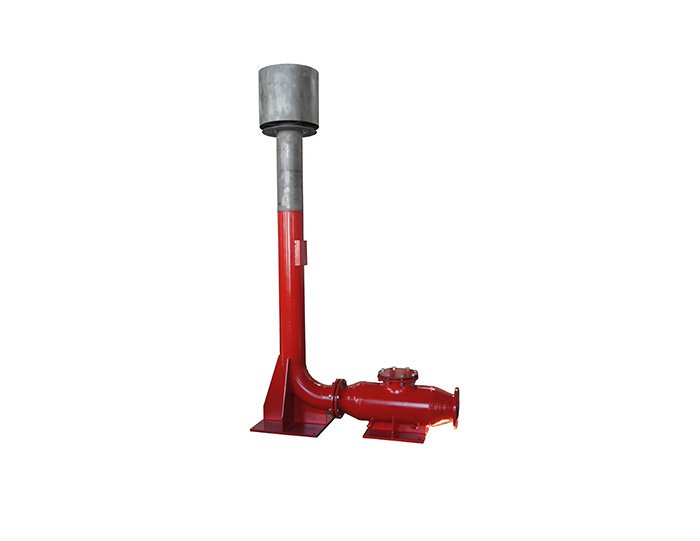 Flare Ignition Device
Flare Ignition Device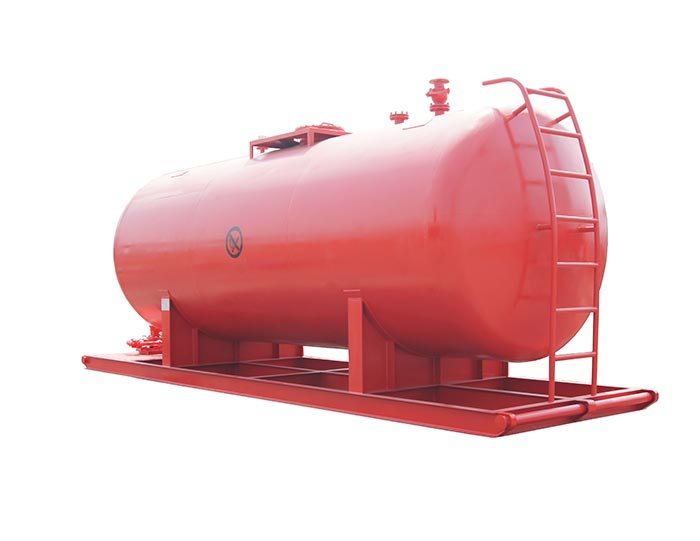  Diesel Tank
Diesel Tank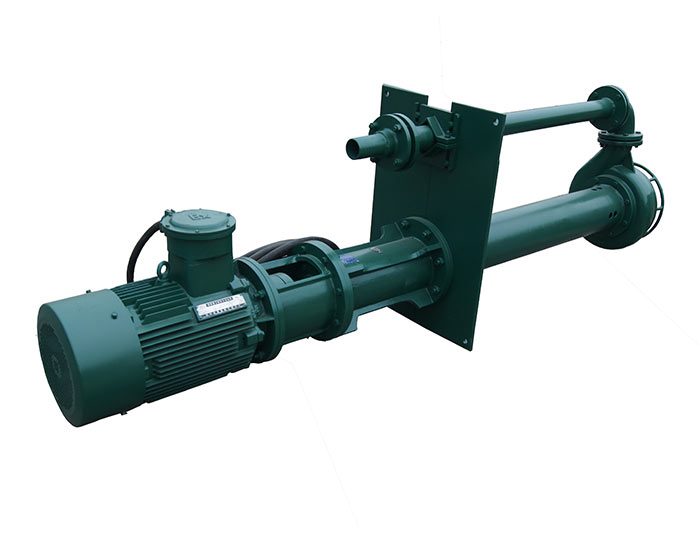  Submersible Slurry Pump
Submersible Slurry Pump