Drilling waste management is a critical aspect of oil and gas operations, focusing on minimizing environmental impact and adhering to regulatory requirements. The process involves the treatment, recycling, and disposal of drilling waste, including drilling cuttings and fluids. This article explores the various methods and technologies used in drilling waste management,
emphasizing the importance of sustainable practices.

Understanding Drilling Waste and Its Impact
What is Drilling Waste?
Drilling waste primarily consists of drilling fluids and cuttings generated during the drilling process. Drilling fluids, also known as drilling mud, are used to lubricate and cool the drill bit, maintain well pressure, and remove cuttings from the wellbore. Drilling cuttings are the fragments of rock and soil excavated during drilling operations. Both components need proper management to prevent environmental contamination.
Environmental Concerns of Drilling Waste
Improper disposal of drilling waste can lead to significant environmental problems, including soil and water pollution, habitat destruction, and negative impacts on local communities and wildlife. Drilling fluids often contain harmful chemicals, and cuttings may be contaminated with hydrocarbons and heavy metals. Therefore, effective drilling waste management is essential to mitigate these risks and promote environmental sustainability.

Methods of Drilling Waste Management
Solid Control Systems
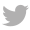
Solid control systems are used to separate drilling cuttings from the drilling fluid, allowing the fluid to be recycled and reused. This process involves several stages of separation, including shale shakers, hydrocyclones, and centrifuges. By efficiently removing solids, solid control systems reduce the volume of waste and enhance the efficiency of drilling operations.
Cuttings Re-Injection (CRI)
Cuttings re-injection is a popular method of disposing of drilling cuttings and other waste materials by injecting them into a dedicated subsurface formation. This technique minimizes surface environmental impact and is particularly useful in environmentally sensitive areas or offshore drilling sites where space is limited. CRI is considered a safe and effective method of waste disposal, as it prevents contaminants from reaching the surface or water bodies.
Thermal Desorption Units (TDUs)
Thermal desorption is a process that uses heat to separate hydrocarbons and water from drilling cuttings. The cuttings are heated in a controlled environment, causing the hydrocarbons to vaporize, which are then collected and condensed for reuse. The remaining solids are typically non-hazardous and can be disposed of safely. TDUs are highly effective in reducing the volume of drilling waste and recovering valuable hydrocarbons.
Bioremediation
Bioremediation is an environmentally friendly method of treating drilling waste by using microorganisms to degrade organic contaminants. This process can be applied to both drilling fluids and cuttings and is particularly effective for treating oil-based mud and cuttings. Bioremediation offers a sustainable solution for drilling waste management, as it converts harmful substances into non-toxic compounds through natural processes.
Landfarming and Land Spreading
Landfarming and land spreading are methods of disposing of drilling waste by spreading it over a designated area of land. The waste is then mixed with soil and left to degrade naturally over time. While these methods can be cost-effective and simple, they require careful management to prevent soil and water contamination. They are more suitable for non-hazardous waste and in areas with low environmental sensitivity.

Advancements in Drilling Waste Management Technology
Waste Minimization and Recycling
Recent advancements in drilling waste management focus on waste minimization and recycling. Technologies such as closed-loop systems are designed to minimize waste generation by reusing drilling fluids and reducing the volume of cuttings produced. Additionally, recycling and reusing drilling fluids can significantly reduce the environmental footprint of drilling operations.
Automated Monitoring and Control Systems
Automated monitoring and control systems enable real-time tracking of drilling waste parameters, ensuring compliance with environmental regulations and optimizing waste management processes. These systems help identify potential issues early, allowing for quick corrective actions and improving overall efficiency and safety.
The Future of Drilling Waste Management
The future of drilling waste management is geared towards sustainability and stricter environmental compliance. As environmental regulations become more stringent, the industry is adopting innovative technologies and practices to minimize waste, reduce environmental impact, and promote sustainable operations. Companies are increasingly investing in research and development to find new ways to manage drilling waste effectively and responsibly.
Collaboration between industry stakeholders, regulatory bodies, and environmental organizations is essential to developing best practices and standards for drilling waste management. By sharing knowledge and experiences, the industry can enhance its ability to manage drilling waste efficiently and sustainably, ensuring a cleaner and safer environment for future generations.
Drilling waste management is a vital component of responsible oil and gas operations, aiming to minimize environmental impact and ensure regulatory compliance. By employing advanced technologies and sustainable practices, the industry can effectively manage drilling waste, reduce its environmental footprint, and contribute to a cleaner and more sustainable future. Effective drilling waste management not only protects the environment but also enhances operational efficiency and reduces costs, making it a crucial aspect of modern drilling operations.
 Linear Motion Shale Shaker In Drilling Rig
Linear Motion Shale Shaker In Drilling Rig  Oilfield Mud Cleaner
Oilfield Mud Cleaner  Drilling Fluid Decanter Centrifuge
Drilling Fluid Decanter Centrifuge  Drilling Mud Desander
Drilling Mud Desander  Hydrocyclone Desilter
Hydrocyclone Desilter  Centrifugal Pump/Centrifugal Mud Pump
Centrifugal Pump/Centrifugal Mud Pump  Shear Pump
Shear Pump  Jet Mud Mixer
Jet Mud Mixer  Horizontal Mud Agitator
Horizontal Mud Agitator  Constant Pressure Drilling Fluid Mud Gas Separator
Constant Pressure Drilling Fluid Mud Gas Separator  Mud Gun
Mud Gun  Mud Tank
Mud Tank  Solids Control System Vacuum Degasser
Solids Control System Vacuum Degasser  Flare Ignition Device
Flare Ignition Device  Diesel Tank
Diesel Tank  Submersible Slurry Pump
Submersible Slurry Pump