Understanding the Components of the Mud System in Drilling Operations
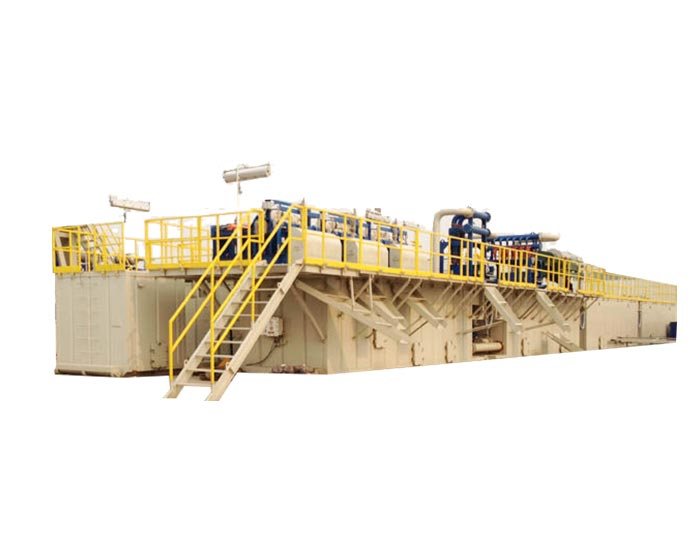
In the field of drilling for oil and gas, the mud system plays a crucial role in ensuring the efficiency and safety of drilling operations. The mud system, often referred to as the drilling fluid system, consists of various components that work together to manage the properties of the drilling fluid. This article will explore the essential components of a mud system and their functions.
1. Drilling Fluids
At the heart of the mud system is the drilling fluid itself, commonly known as mud. Drilling fluids can be classified into three main categories water-based, oil-based, and synthetic-based fluids. Each type has its advantages and disadvantages, depending on the drilling conditions and environmental considerations. The primary functions of drilling fluids include
- Cooling and Lubricating As the drill bit penetrates the ground, friction generates heat. The mud cools the bit and reduces wear on the drilling equipment.
- Cuttings Removal The fluid carries cuttings from the borehole to the surface, where they can be removed and analyzed.
- Suppressing Formation Pressure The mud creates hydrostatic pressure that helps prevent the collapse of the borehole and keeps formation fluids from entering the wellbore.
2. Mud Pumps
Mud pumps are vital components of the mud system, responsible for circulating the drilling fluid through the system. These pumps are usually positive displacement pumps that maintain a steady flow of mud to the drill bit and back to the surface. High-pressure capabilities are essential to ensure that the drilling fluid reaches the required depths, overcoming the pressure exerted by the geological formations.
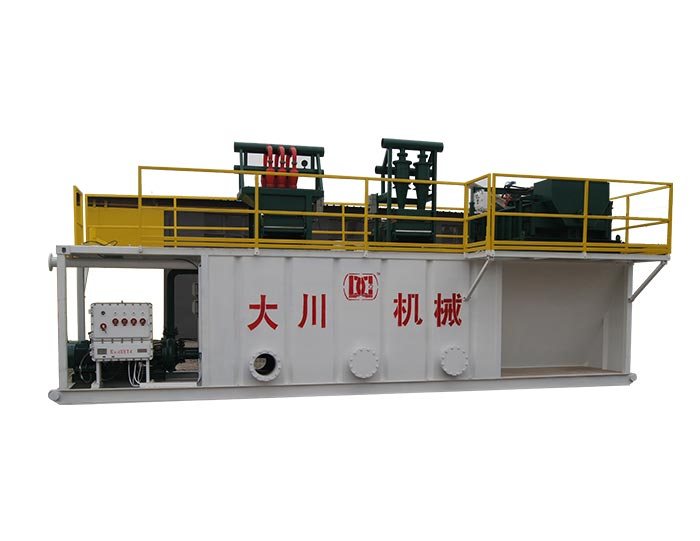
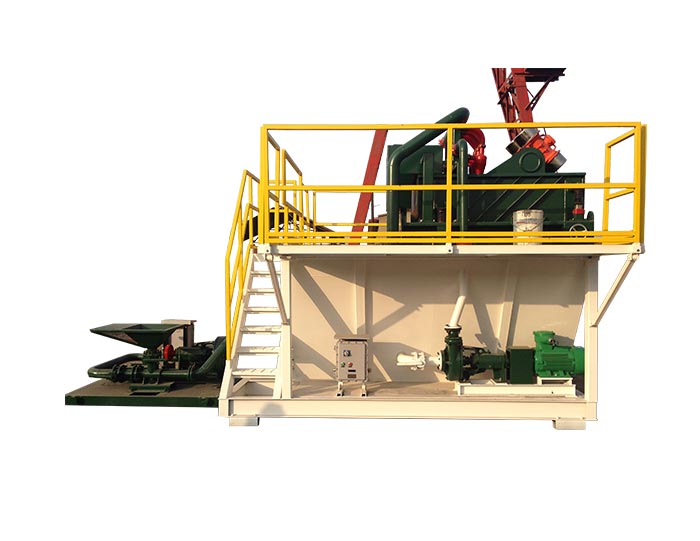
3. Mud Mixing and Conditioning Equipment
Before being pumped into the well, drilling fluids must be mixed and conditioned to achieve the desired properties. This process includes the addition of various chemicals and additives to improve performance. Equipment such as mud tanks, mixing hoppers, and agitators are used in this stage. The mud is conditioned to ensure proper density, viscosity, and water content, which are crucial for effective drilling.
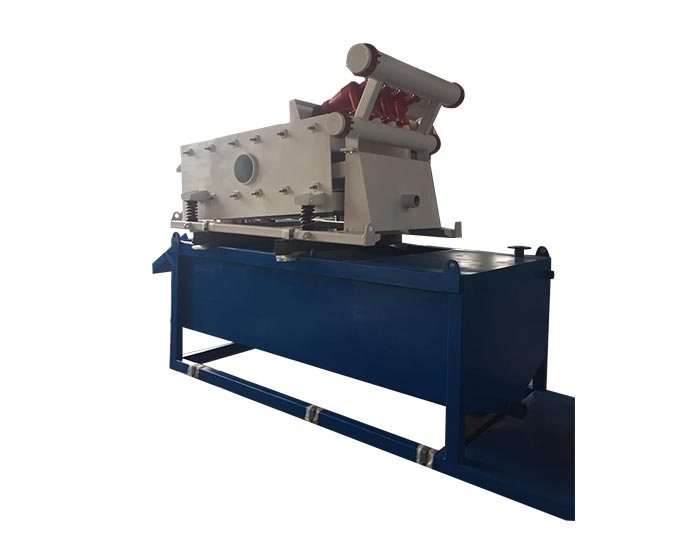
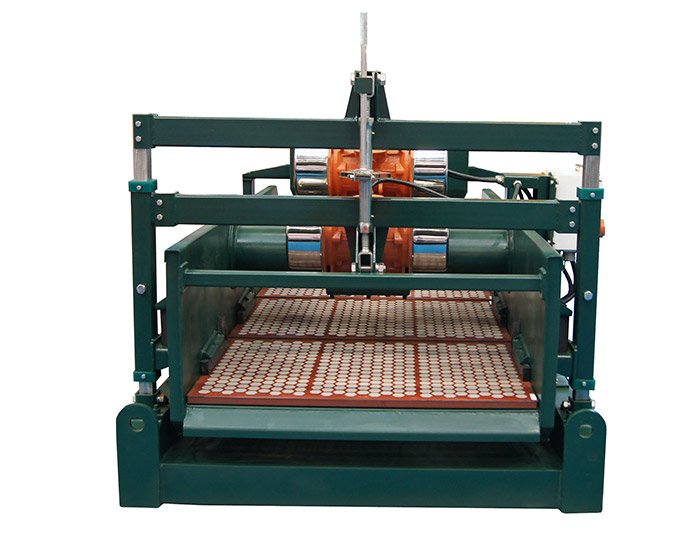
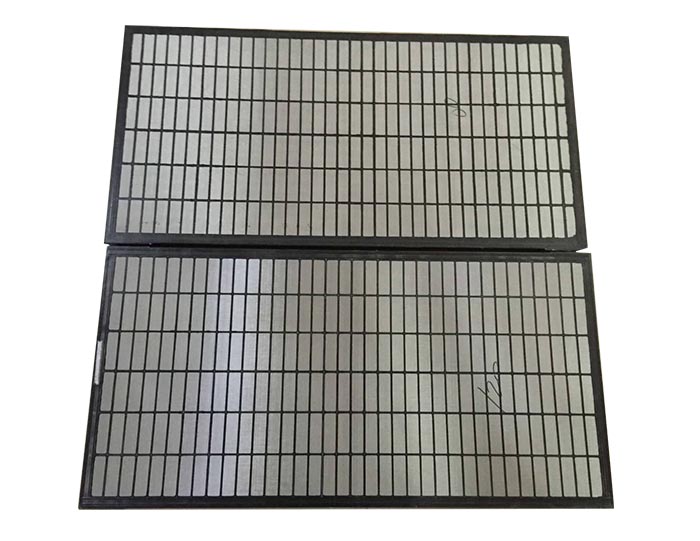
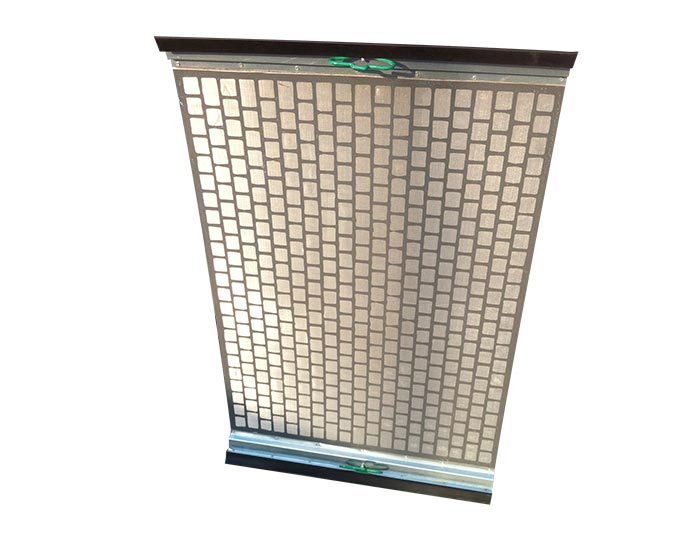
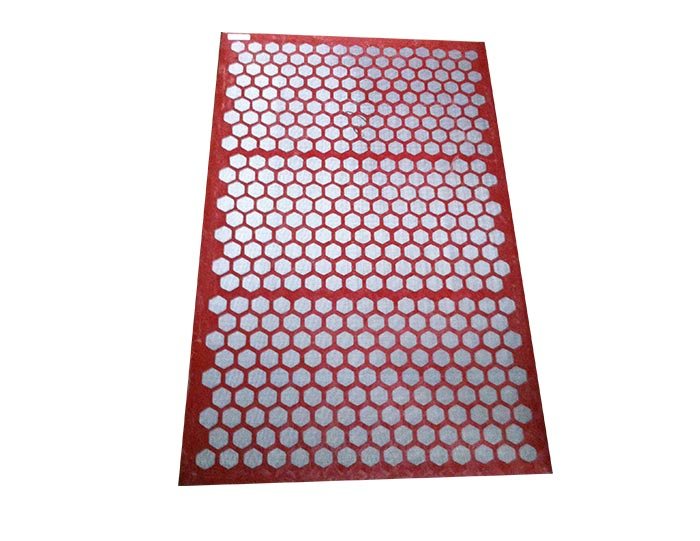
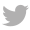
4. Shale Shakers
mud system consist of
Shale shakers are essential for removing solid cuttings from the drilling fluid after it has been circulated. These machines use screens to separate the cuttings from the liquid mud, allowing the fluid to be reused. Effective shale shakers help maintain the efficiency of the mud system by ensuring that the mud remains clean and suitable for continued circulation.
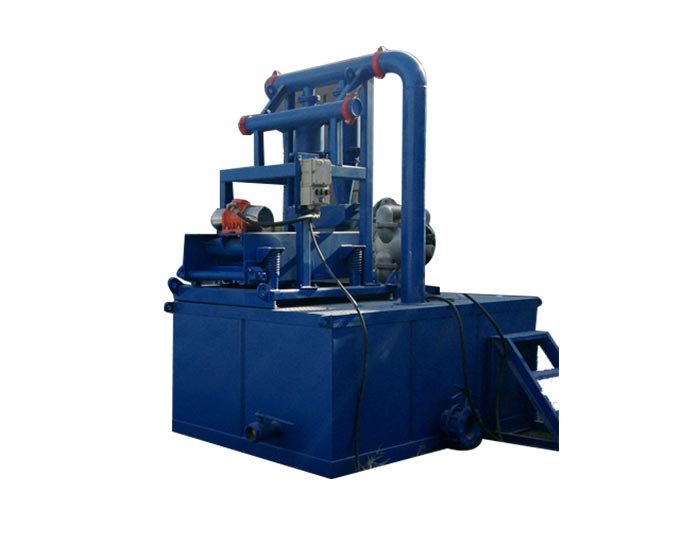
5. Desanders and Desilters
These components further enhance the mud\'s cleanliness and quality. Desanders remove larger particles, while desilters specialize in filtering out smaller solids. By maintaining the appropriate particle size and concentration in the drilling fluid, these devices help optimize the mud’s performance, thus improving overall drilling efficiency.
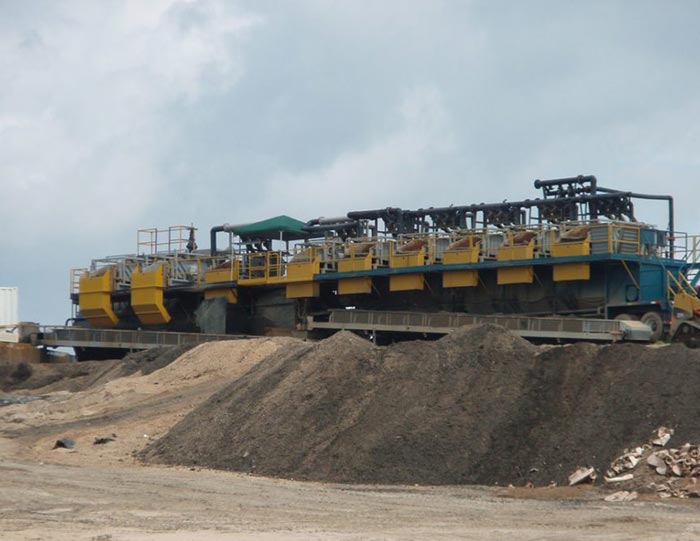
6. Mud Returns System
This system is responsible for returning used drilling fluid back to the surface after it has circulated through the wellbore. It usually consists of a series of pipes and hoses that transport the fluid from the drill site back to storage tanks or to the shale shakers for cleaning.
7. Additive Storage and Mixing Systems
To maintain optimal mud properties, various additives are often mixed into the drilling fluid. These can include agents to enhance viscosity, reduce fluid loss, or provide filtration control. The storage and mixing systems for these additives are crucial to ensure that they can be accurately measured and blended into the mud.
Conclusion
The mud system is a complex yet essential component of modern drilling operations, composed of multiple interrelated parts that work seamlessly to ensure efficiency and safety. Understanding the various elements, from the drilling fluids to the pumps and conditioning equipment, is crucial for professionals in the oil and gas industry. By effectively managing the mud system, drilling engineers can optimize operations, reduce costs, and enhance safety on the rig.
 Linear Motion Shale Shaker In Drilling Rig
Linear Motion Shale Shaker In Drilling Rig  Oilfield Mud Cleaner
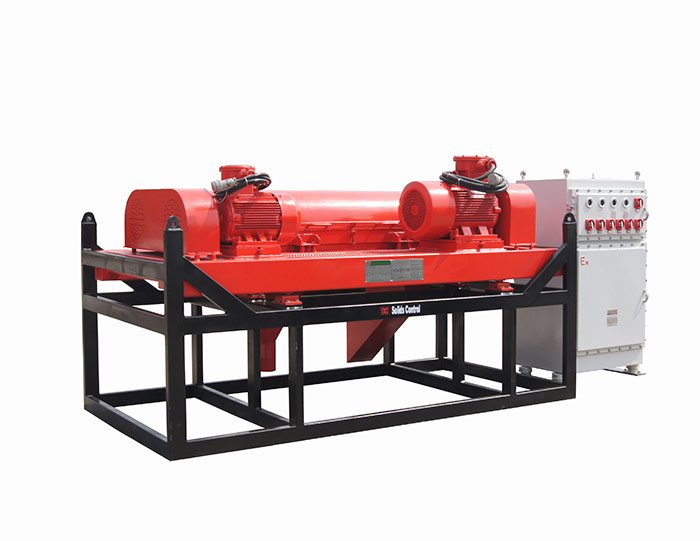
Oilfield Mud Cleaner  Drilling Fluid Decanter Centrifuge
Drilling Fluid Decanter Centrifuge Drilling Mud Desander
Hydrocyclone Desilter
Centrifugal Pump/Centrifugal Mud Pump
Shear Pump
Jet Mud Mixer
Horizontal Mud Agitator
Constant Pressure Drilling Fluid Mud Gas Separator
Mud Gun
 Mud Tank
Mud Tank Solids Control System Vacuum Degasser
 Flare Ignition Device
Flare Ignition Device  Diesel Tank
Diesel Tank  Submersible Slurry Pump
Submersible Slurry Pump