Conductive Adhesive Tape An Essential Tool for Modern Electronics
In the rapidly evolving world of electronics, the demand for effective and reliable materials is more critical than ever. One such material that has gained prominence in recent years is conductive adhesive tape. This versatile product combines the advantages of adhesive tape with the ability to conduct electricity, making it an invaluable tool in various applications across multiple industries.
Conductive adhesive tape consists of a substrate that is typically made from a flexible material such as foam, fabric, or plastic, coated with a conductive adhesive. The conductive nature of the adhesive is usually a result of incorporating metal particles—such as copper, aluminum, or silver—into the adhesive matrix. This unique combination allows the tape to maintain strong electrical connections while also adhering securely to surfaces.
One of the primary applications of conductive adhesive tape is in the electronics industry. It is widely used for grounding and shielding applications. Grounding is essential for preventing electrical interference in devices and ensuring safety in both consumer and industrial electronics. Conductive adhesive tape provides a simple and effective solution for creating a reliable ground connection, especially in devices where traditional grounding methods may be impractical.
Additionally, conductive adhesive tape is frequently utilized for electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding. As electronic devices become smaller and more powerful, the risk of interference from electromagnetic waves increases. By applying conductive tape to critical areas of an electronic assembly, designers can effectively reduce the impact of EMI, ensuring that devices operate properly and do not disrupt nearby equipment. This is particularly important in sensitive environments such as hospitals or research labs, where electronic noise can lead to significant errors.
conductive adhesive tape

Another notable aspect of conductive adhesive tape is its ease of use. Unlike soldering or other permanent connections, conductive tape allows for quick and easy application, enabling engineers and technicians to make modifications or repairs on-the-fly. This flexibility is particularly valuable in prototype development, where design changes are common, and speed is crucial. Users can cut the tape to the desired length, peel off the backing, and apply it directly to the target surface, significantly reducing downtime.
Conductive adhesive tape also finds applications in the realm of wearable technology. As health monitoring devices and smart textiles become increasingly popular, the need for reliable conductive materials that can withstand bending and stretching has grown. Conductive adhesive tape provides a lightweight and flexible solution for connecting sensors and circuits in wearable devices. Its ability to conform to various surfaces means that it can be used in innovative product designs that were previously deemed infeasible.
Furthermore, the growth of the Internet of Things (IoT) has sparked new opportunities for conductive adhesive tape. As more devices become interconnected, the need for robust and reliable electrical connections becomes paramount. Conductive adhesive tape can be used to simplify the assembly of IoT devices, ensuring that connections remain intact even with the vibrations and movements they may encounter during use.
In conclusion, conductive adhesive tape is a multifaceted material that plays a critical role in the advancement of modern electronics. Its combination of electrical conductivity, adhesive properties, and ease of use makes it an essential component for grounding, shielding, and connecting various electronic devices. As technology continues to evolve and the demand for innovative solutions grows, conductive adhesive tape is poised to remain a key player in the landscape of electronic manufacturing and design. Whether in consumer electronics, industrial applications, or wearable tech, this innovative material is here to stay, helping to shape the future of connectivity and functionality in the digital age.
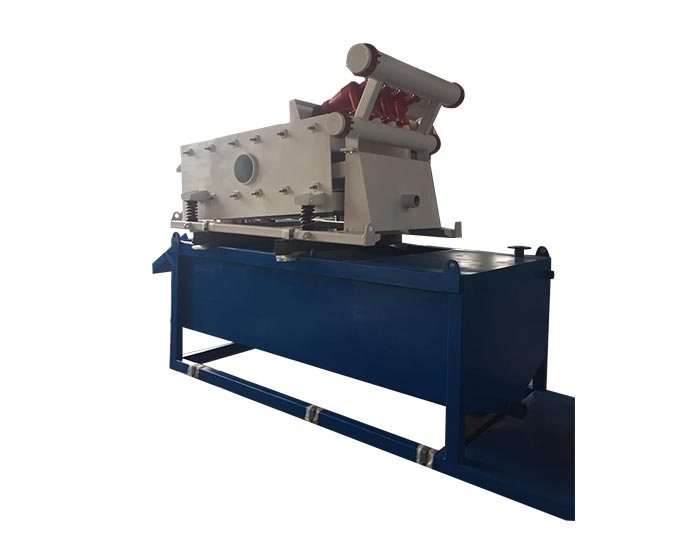
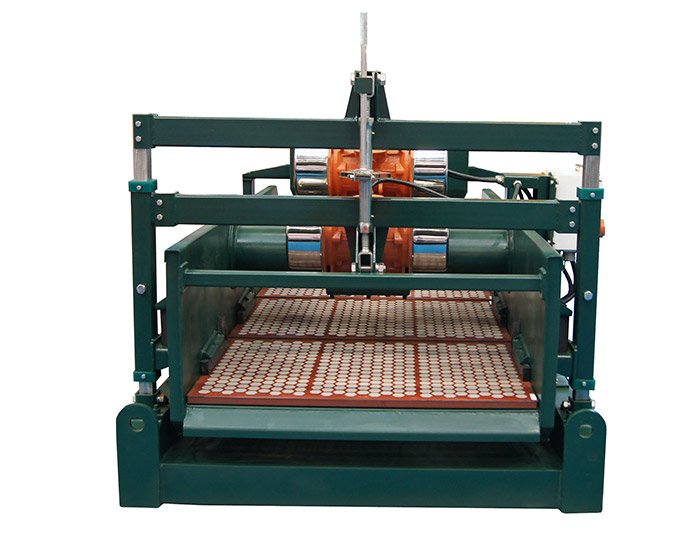
 Linear Motion Shale Shaker In Drilling Rig
Linear Motion Shale Shaker In Drilling Rig  Oilfield Mud Cleaner
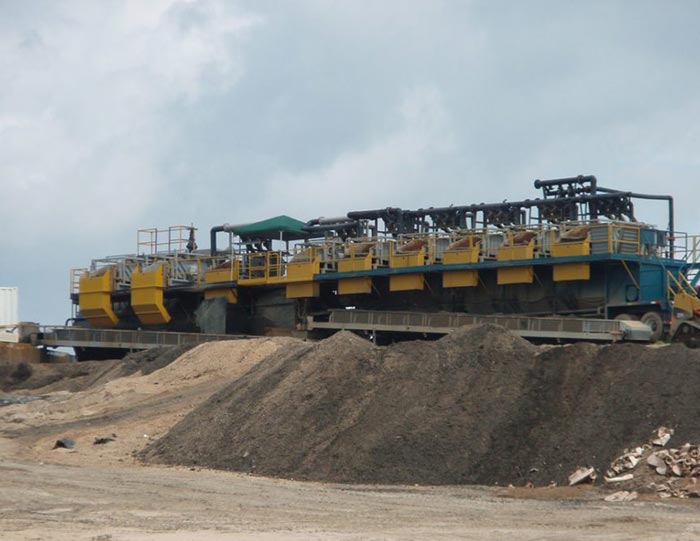
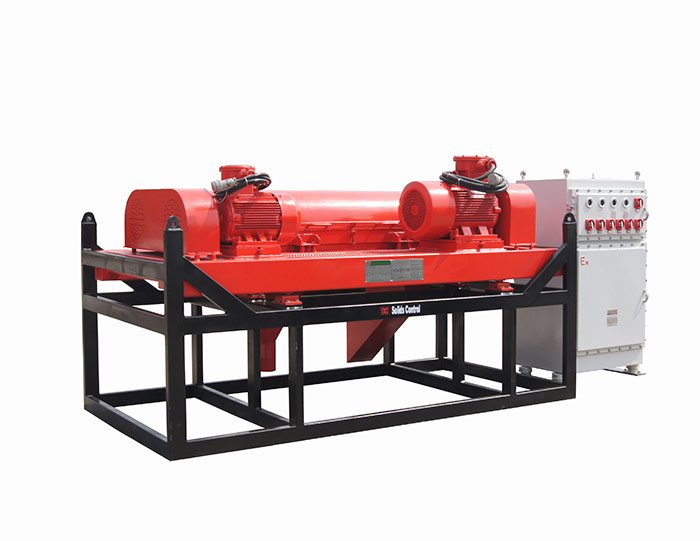
Oilfield Mud Cleaner  Drilling Fluid Decanter Centrifuge
Drilling Fluid Decanter Centrifuge Drilling Mud Desander
Hydrocyclone Desilter
Centrifugal Pump/Centrifugal Mud Pump
Shear Pump
Jet Mud Mixer
Horizontal Mud Agitator
Constant Pressure Drilling Fluid Mud Gas Separator
Mud Gun
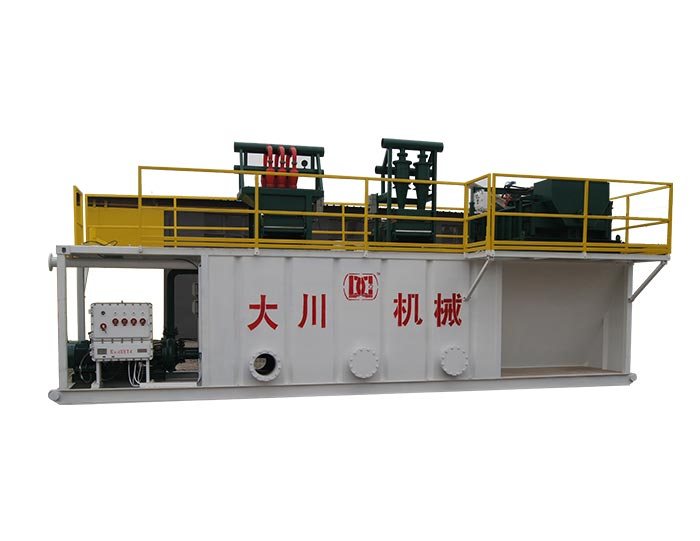
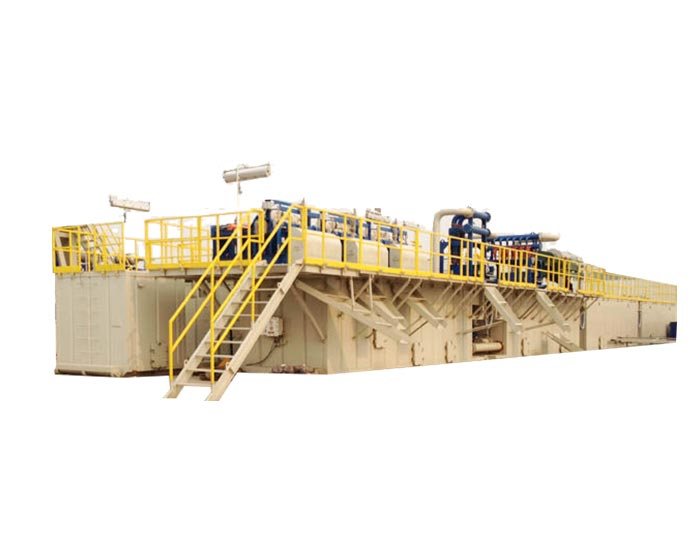
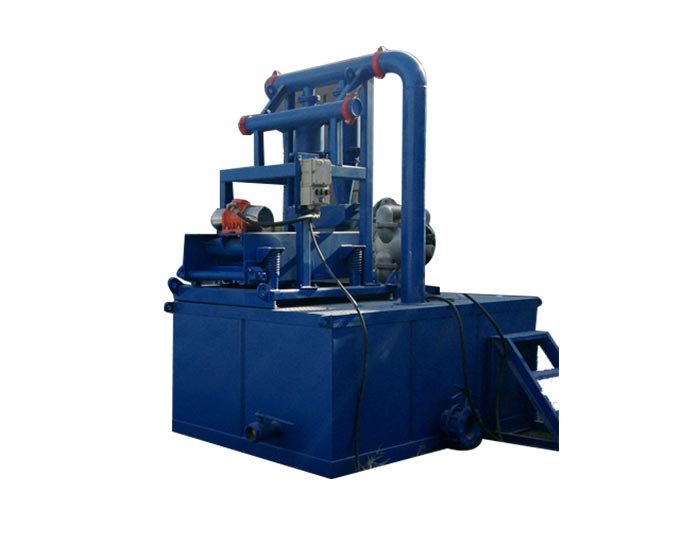
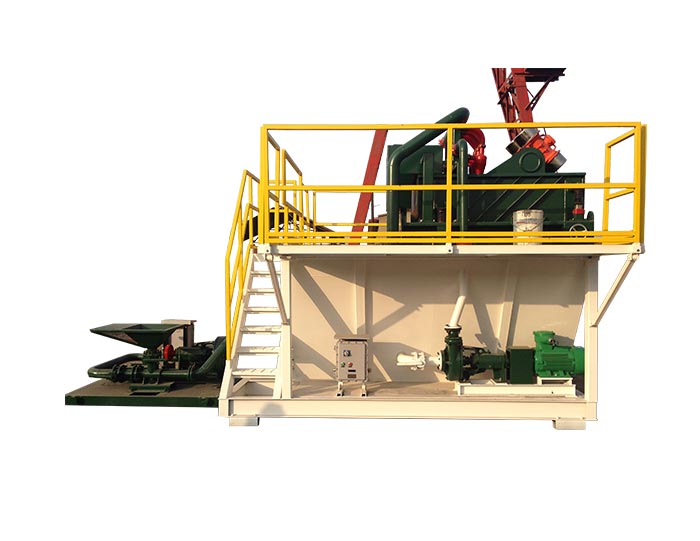
 Mud Tank
Mud Tank Solids Control System Vacuum Degasser
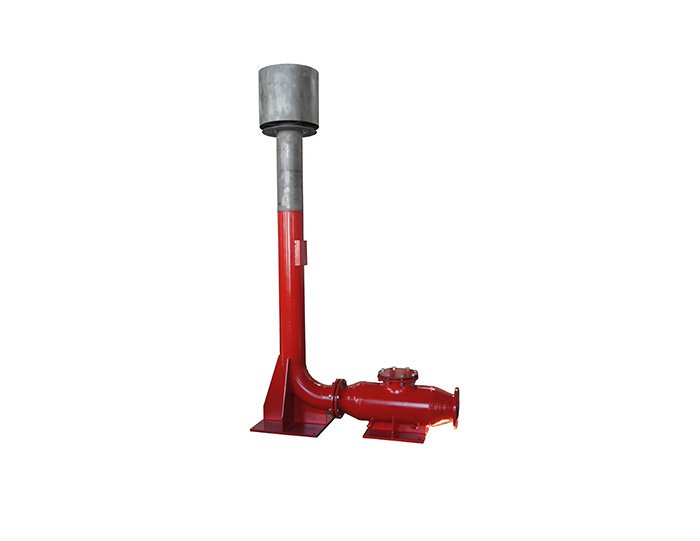 Flare Ignition Device
Flare Ignition Device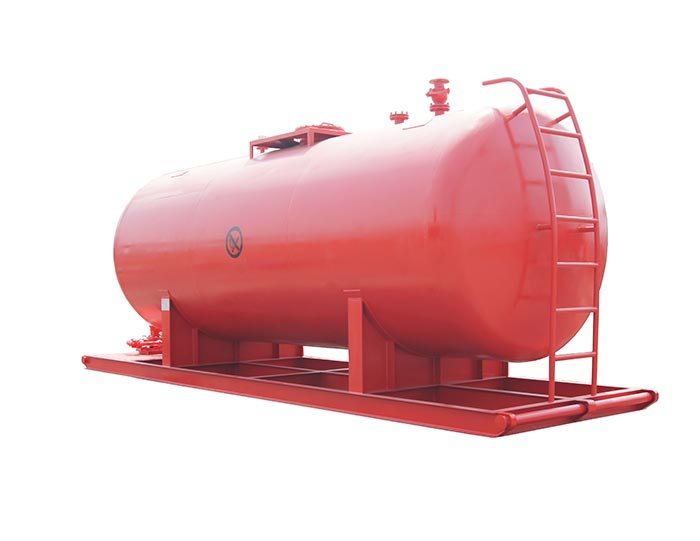  Diesel Tank
Diesel Tank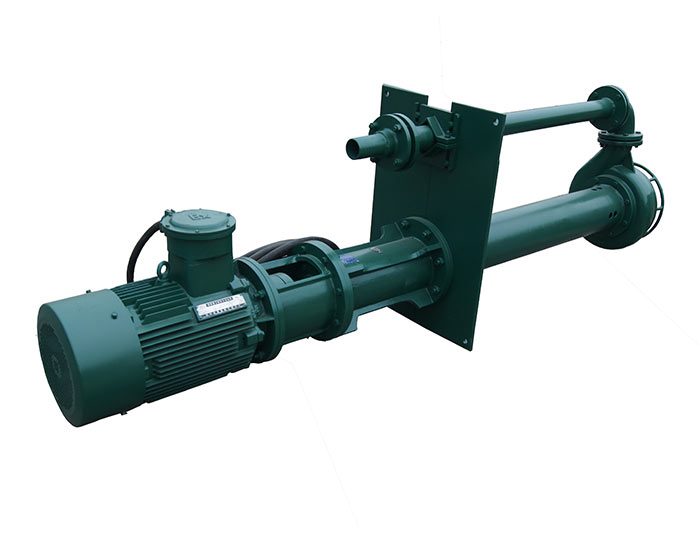  Submersible Slurry Pump
Submersible Slurry Pump